
#
Lab 8 - STP, Summarization, & DHCP
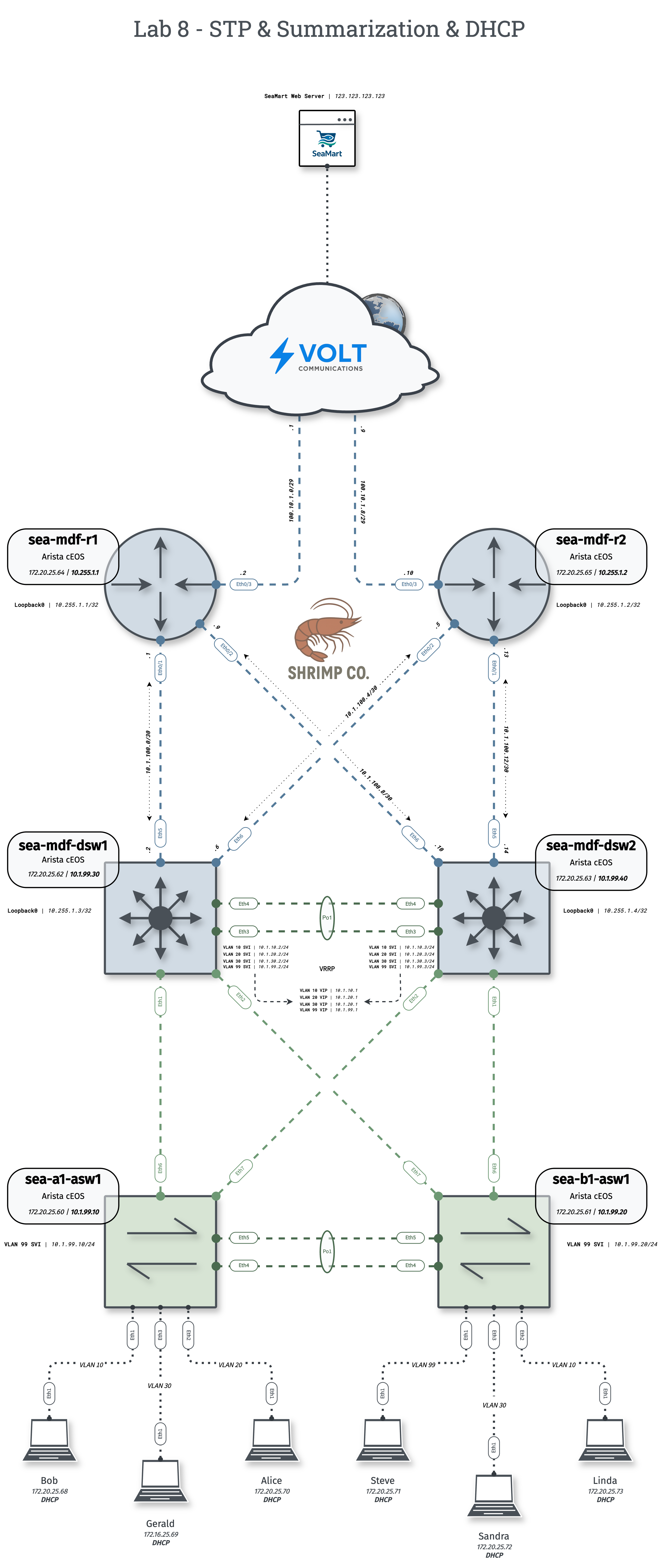
Shrimp Co.'s growing workforce requires more efficient Layer 2 resilience, streamlined routing, and simplified host IP management. Configure spanning-tree for redundancy, summarize routes for scalability, and deploy DHCP services for VLANs across the network.
Tip: Individual topology files are available in the diagrams folder on my Github
#
Configuration Tasks
#
Layer 2 Configuration
Ensure access ports, trunks, VLAN databases, and port-channels are configured to span Layer 2 domain across all access and distribution switches.
- VLAN 10 – Sales
- VLAN 20 – Engineering
- VLAN 30 – Marketing (New)
- VLAN 99 – IT
#
1. Configure Rapid Per-VLAN Spanning-Tree
- Enable PVST+ on all switches.
- Assign root bridge priorities so that:
sea-mdf-dsw1is the root for VLANs 10 and 99sea-mdf-dsw2is the root for VLANs 20 and 30
- Verify root bridge election and port roles using the appropriate show commands.
#
2. Configure Distribution Switches
- Configure VRRP according to the diagram, load-balancing active gateways between
dsw1anddsw2and implementing md5 authentication - On
sea-mdf-dsw1andsea-mdf-dsw2, use a single network statement to advertise a single summary route into OSPF. - Ensure summary route is seen on
sea-mdf-r1andsea-mdf-r2 - Utilize
passive-interface defaultunder your OSPF process configuration and enable adjacencies on only on Eth5, Eth6, and VLAN 99.
#
3. Configure Routers
- Configure OSPF to form adjacencies on Eth0/1 and Eth0/2
- Originate a default route into OSPF with a next-hop of your ISP
- Set up a DHCP server and pool for each VLAN (10, 20, 30, 99) on either
sea-mdf-r1orsea-mdf-r2. - Use DHCP relay on SVI's to forward client requests to your DHCP server.
- Exclude gateway IP addresses from your DHCP pools.
Linux host DHCP commands
sudo dhclient -v eth1- Requests DHCP lease + verbose output flagsudo dhclient -r eth1- Release existing lease
#
Success Criteria
- Spanning Tree
sea-mdf-dsw1is root bridge for VLAN 10,20sea-mdf-dsw2is root bridge for VLAN 30,99
- Routing
- Routers are learning a single summary route for all four departments at Shrimp Co.
- All Loopbacks are reachable from hosts.
- You can curl http://seamart.com from a host that got DHCP
- DHCP
- All hosts receive a DHCP lease
- Capture and inspect a DHCP Discover and Offer exchange in a tcpdump on an access switch |
tcpdump interface [ethernet X] filter udp - Configure OSPF with neighbor authentication
- Exclude .1 through .9 from being handed out as DHCP addresses and set a lease time of one day.
#
Verification Commands
# Spanning-tree verification
show spanning-tree vlan [10]
show spanning-tree [detail]
show spanning-tree blockedports# OSPF
show ip ospf database summary
show ip route ospf
show ip ospf neighbor
show ip ospf interface [Ethernet5]
# DHCP bindings
show ip dhcp binding
# IP and default gateway
ip route show
# Gateway reachability
ping <default_gateway>
# Internet reachability test
curl http://seamart.com
#
Questions to Explore
- How does spanning-tree decide which ports go into a blocking state?
- What is the benefit of route-summarization?
- Why is it necessary for us to run OSPF in this environment over EIGRP?
- Are there other routing protocols that could also work?
